
iBOMMA: A Detailed Article
iBOMMA: A Detailed Article
Anime Girlies: Unveiling the Kawaii World of Animated Characters
25 photos of Anime Girlies
Popular Stories

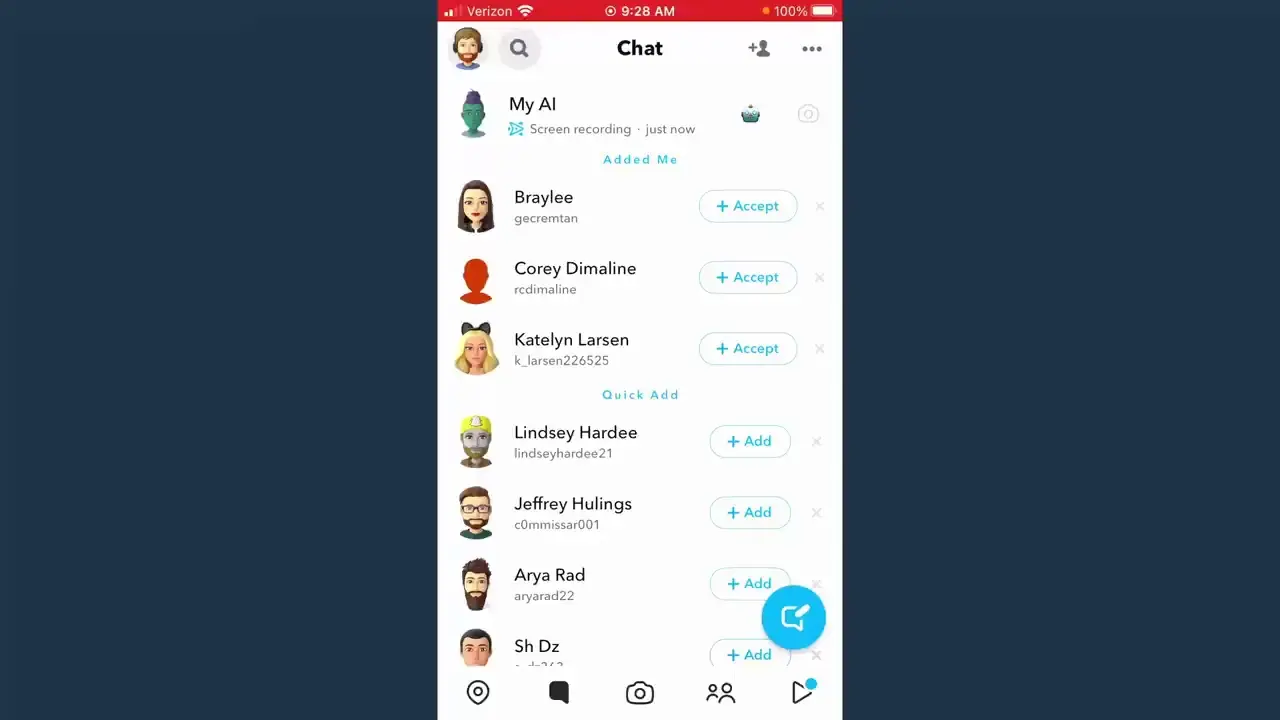
How to Remove ‘My AI’ from Snapchat
How to Delete My AI in Snapchat “Snapchat’s My AI Chatbot: A Convenient Tool with Privacy Considerations Snapchat’s My AI chatbot, initially exclusive to Snapchat+



Anime Girlies: Unveiling the Kawaii World of Animated Characters
25 photos of Anime Girlies
All About
Photography
How to Remove ‘My AI’ from Snapchat
iBOMMA: A Detailed Article
Travel & Explore the world

How to Remove ‘My AI’ from Snapchat
How to Delete My AI in Snapchat “Snapchat’s My AI Chatbot: A Convenient Tool with Privacy Considerations Snapchat’s My AI chatbot, initially exclusive to Snapchat+



Anime Girlies: Unveiling the Kawaii World of Animated Characters
25 photos of Anime Girlies

10 Best Shopify Apps For Your Ecommerce
Struggling to pick the perfect Shopify apps for your ecommerce store? Look no further! This snippet explores 10 powerful apps to boost sales (Klaviyo, Yotpo),

Matthew Patel: More Than Just an Evil Ex
The name Matthew Patel might conjure up images of a flamboyant skateboarder with a killer haircut and a fierce competitive streak. But to simply label

What is Gap Insurance?
Understanding Gap Insurance: Bridging the Financial Divide In the complex landscape of auto insurance, one term that often surfaces is “Gap Insurance.” But what exactly


Explore and travel the world

How to Fix Error Code: m7111-1331-5059

Iman Gadzhi Age, Boyfriend, Height, Bio, NetWorth, Wiki

11 Best Microsoft Word Alternatives

201+ Best Pluto TV Channels List (Free & Paid) in April 2024

10 Best Banks For Education Loan In United States of America
Beauty Tips and Tricks

How to Remove ‘My AI’ from Snapchat
How to Delete My AI in Snapchat “Snapchat’s My AI Chatbot: A Convenient Tool with Privacy Considerations Snapchat’s My AI chatbot, initially exclusive to Snapchat+

iBOMMA: A Detailed Article
iBOMMA: A Detailed Article


Anime Girlies: Unveiling the Kawaii World of Animated Characters
25 photos of Anime Girlies
Glorious Fashion

What is Invideo
InVideo is a cloud-based video editing platform that enables users to create professional-looking videos without any prior experience. It offers a wide range of features,

10 Best Platforms to Hire Professional Designers
Need a logo, website, or video? This summary lists top platforms to hire creative freelancers (Bunny Studio, Fiverr, Upwork) or run design contests (99designs, DesignCrowd).

Dina Kalanta Age, Boyfriend, Height, Bio, Net Worth, Wiki
Dina Kalanta Age Networth 2023 It is estimated that Dina Kalanta has a net worth of around $4 Million. You will be able to get accurate information about Dina

Food & Drinks From Around the World
Watch Animag's Video Channel





